What you need to know about Phuket
Phuket Region Map
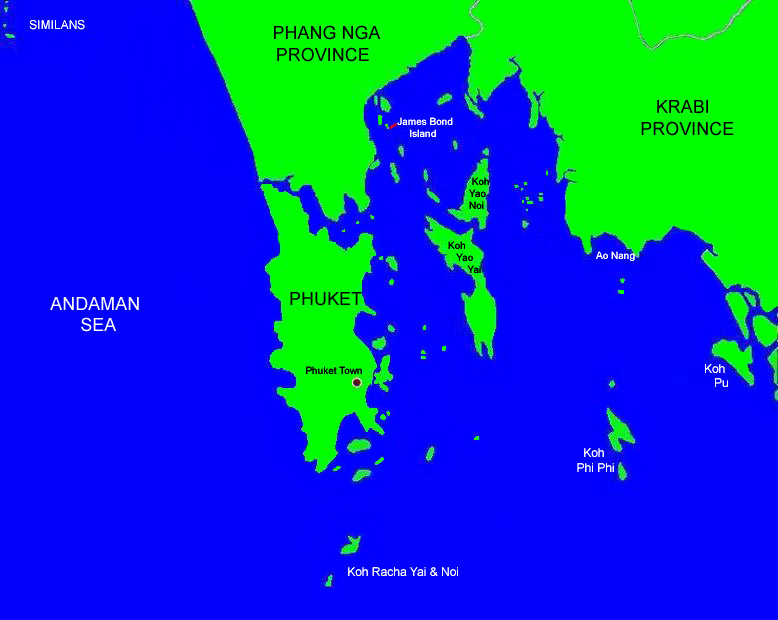
Phuket is one of the southern provinces (changwat) of Thailand. It consists of the island of Phuket, the country’s largest island, and another 32 smaller islands off its coast. It lies off the west coast of Thailand in the Andaman Sea. Phuket Island is connected by the Sarasin Bridge to Phang Nga Province to the north. The next nearest province is Krabi, to the east across Phang Nga Bay.
Phuket Province has an area of 576 square kilometres (222 sq mi), somewhat less than that of Singapore, and is the second-smallest province of Thailand. It formerly derived its wealth from tin and rubber, and enjoys a rich and colorful history. The island was on one of the major trading routes between India and China, and was frequently mentioned in foreign ship logs of Portuguese, French, Dutch, and English traders. The region now derives much of its income from tourism.
Population: 386,605 (2015)
Language
People in general use southern Thai dialect, which sounds more succinct and is spoken faster than the central Thai. English is understood in tourist areas. The most important products of Phuket are marine products, latex, rubber, fuel oil and frozen fish.
Currency
Thailand’s currency is Baht. Bills come in denominations of 1000, 500, 100, 50 and 20. Coins are 10, 5, 1 and tiny satangs. Satangs are quarter fractions of 1 and are not widely used. Most international currencies and Travellers Cheques can be exchanged at banks or local moneychangers. Major credit cards are accepted in major establishments as well as at moneychangers.
History
The Portuguese explorer Fernão Mendes Pinto arrived in Siam in the year 1545 (16th century). His accounts of the country go beyond Ayutthaya and included a reasonably detailed account of ports in the south of the Kingdom as well. Pinto was one of the first European explorers to mention Phuket in any detail, in his travel accounts. He referred to the island as ‘Junk Ceylon’, a name the Portuguese used for Phuket Island in their maps. Junk Ceylon is mentioned seven times in Mendes Pinto’s accounts. Pinto said that Junk Ceylon was a destination port where trading vessels made regular stops for supplies and provisions, however, during the mid-16th century, the island was in decline due to pirates and often rough and unpredictable seas, which deterred merchant vessels from visiting Junk Ceylon. Pinto mentioned several other notable port cities in his accounts, including Patani and Ligor,which is modern day Nakhon Si Thamarat.
In the 17th century, the Dutch, English and, after the 1680s, the French, competed for the opportunity to trade with the island of Phuket (then known as “Jung Ceylon”), which was a rich source of tin. In September 1680, a ship of the French East India Company visited Phuket and left with a full cargo of tin.
A year or two later, the Siamese King Narai, seeking to reduce Dutch and English influence, named as governor of Phuket a French medical missionary, Brother René Charbonneau, a member of the Siam mission of the Société des Missions Étrangères. Charbonneau remained as governor until 1685.
In 1685, King Narai confirmed the French tin monopoly in Phuket to their ambassador, the Chevalier de Chaumont. Chaumont’s former maître d’hôtel, Sieur de Billy, was named governor of the island. However, the French were expelled from Siam after the 1688 Siamese revolution. On 10 April 1689, Desfarges led an expedition to re-capture Phuket to restore French control in Siam. His occupation of the island led to nothing, and Desfarges returned to Puducherry in January 1690.
The Burmese attacked Phuket in 1785. Francis Light, a British East India Company captain passing by the island, notified the local administration that he had observed Burmese forces preparing to attack. Than Phu Ying Chan, the wife of the recently deceased governor, and her sister Mook (คุณมุก) assembled what local forces they could. After a month-long siege of the capital city, the Burmese were forced to retreat on 13 March 1785. The women became local heroines, receiving the royal titles Thao Thep Kasattri and Thao Si Sunthon from a grateful King Rama I. During the reign of King Chulalongkorn (Rama V), Phuket became the administrative center of the tin-producing southern provinces. In 1933 Monthon Phuket (มณฑลภูเก็ต) was dissolved and Phuket became a province.
2004 tsunami
On 26 December 2004, Phuket and other nearby areas on Thailand’s western coast suffered extensive damage when they were struck by the Boxing Day tsunami, caused by the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake. The waves destroyed several highly populated areas in the region, killing up to 5,300 people nationwide, and tens of thousands more throughout the Asian region. Some 250 were reported dead in Phuket, including foreign tourists, and as many perhaps as a thousand of the illegal Burmese workers building new beach resorts in the Khao Lak area. Almost all of the major beaches on the west coast, especially Kamala, Patong, Karon, and Kata sustained major damage, with some damage caused to resorts and villages on the island’s southern beaches.
By February 2005 many damaged resorts were back to business, and life slowly returned to normal. Following strenuous recovery programs, no tsunami damage can now be seen except on the most remote beaches.
In early December 2006, Thailand launched the first of the 22 U.S.-made tsunami-detection buoys to be positioned around the Indian Ocean as part of a regional warning system. The satellite-linked deep-sea buoys float 1,000 km (620 mi) offshore, roughly midway between Thailand and Sri Lanka.
Geography
Phuket is the largest island in Thailand. It is in the Andaman Sea in southern Thailand. The island is mostly mountainous with a mountain range in the west of the island from the north to the south. The mountains of Phuket form the southern end of the Phuket mountain range, which ranges for 440 kilometres (270 mi) from the Kra Isthmus.
Although some recent geographical works refer to the sections of the Tenasserim Hills in the isthmus as the “Phuket Range”, these names are not found in classical geographic sources. In addition, the name Phuket is relatively recent having previously been named Jung Ceylon and Thalang. The highest elevation of the island is usually regarded as Khao Mai Thao Sip Song (Twelve Canes), at 529 metres (1,736 ft) above sea level. However it has been reported by barometric pressure readings that there is an even higher elevation (with no apparent name), of 542 meters above sea level, in the Kamala hills behind Kathu waterfall.
Its population was 249,446 in 2000, rising to 525,709 in the 2010 decennial census, the highest growth rate of all provinces nationwide at 7.4 percent annually. Some 600,000 people reside on Phuket currently, among them migrants, international expats, Thais registered in other provinces, and locals. The registered population, however, includes only Thais who are registered in a “tabien baan” or house registration book, which most are not, and the end of 2012 was 360,905 persons.
Phuket is approximately 863 kilometres (536 mi) south of Bangkok, and covers an area of 543 square kilometres (210 sq mi) excluding small islets. It is estimated that Phuket would have a total area of approximately 576 square kilometres (222 sq mi) if all its outlying islands were included. Other islands are: Ko Lone 4.77 square kilometres (1.84 sq mi), Ko Maprao 3.7 square kilometres (1.4 sq mi), Ko Naka Yai 2.08 square kilometres (0.80 sq mi), Ko Racha Noi 3.06 square kilometres (1.18 sq mi), Ko Racha Yai 4.5 square kilometres (1.7 sq mi), and the second biggest, Ko Sire 8.8 square kilometres (3.4 sq mi).
The island’s length, from north to south, is 48 kilometres (30 mi) and its width is 21 kilometres (13 mi).
Seventy percent of Phuket’s area is covered with mountains which stretch from north to south. The remaining 30 percent are plains in the central and eastern parts of the island. It has a total of nine brooks and creeks, but does not have any major rivers.
Forest, rubber, and palm oil plantations cover 60 percent of the island. The west coast has several sandy beaches. The east coast beaches are more often muddy. Near the southernmost point is Laem Phromthep (Thai: แหลมพรหมเทพ)(“Brahma’s Cape”), a popular viewpoint. In the mountainous north of the island is the Khao Phra Thaeo No-Hunting Area, protecting more than 20 km² of rainforest. The three highest peaks of this reserve are the Khao Prathiu (384 metres (1,260 ft)), Khao Bang Pae 388 metres (1,273 ft), and Khao Phara 422 metres (1,385 ft). The Sirinat National Park on the northwest coast was established in 1981 to protect an area of 90 square kilometres (35 sq mi) (68 kilometres (42 mi) marine area), including the Nai Yang Beach where sea turtles lay their eggs.
The most popular (and overcrowded) tourist area on Phuket is Patong Beach on the central west coast, perhaps owing to the easy access to its wide and long beach. Most of Phuket’s nightlife and its shopping is in Patong, and the area has become increasingly developed. Patong means “the forest filled with banana leaves” in Thai. South of Patong lie Karon Beach, Kata Beach, Kata Noi Beach, and around the southern tip of the island, Nai Han Beach and Rawai. To the north of Patong are Kamala Beach, Surin Beach, and Bang Tao Beach. These areas are generally much less developed than Patong. To the southeast is Bon Island and to the south are several coral islands. The Similan Islands lie to the northwest, and the Phi Phi Islands which are part of Krabi Province, to the southeast.
There are 5 main areas for tourists to stay in Phuket, Patong which is the most popular due to its active nightlife, street markets and calm water beaches however this area isn’t for everyone (especially people with families). The quieter areas include Kata, Karon, Rawai and Nai Yang, all with great markets and quieter beach areas.
Climate
Under the Köppen climate classification, Phuket features a tropical monsoon climate (Am). Due to its proximity to the equator, in the course of the year, there is little variation in temperatures. The city has an average annual high of 32 °C (90 °F) and an annual low of 25 °C (77 °F). Phuket has a dry season that runs from December through March and a wet season that covers the other eight months. However, like many cities that feature a tropical monsoon climate, Phuket sees some precipitation even during its dry season. Phuket averages roughly 2,200 millimetres (87 in) of rain.
Economy
Tin mining was a major source of income for the island from the 16th century until petering out in the 20th century. In modern times, Phuket’s economy has rested on two pillars: rubber tree plantations (making Thailand the biggest producer of rubber in the world) and tourism.
Since the 1980s, the sandy beaches on the west coast of the island have been developed as tourist destinations, with Patong, Karon, and Kata being the most popular. Since the 2004 tsunami, all damaged buildings and attractions have been restored. Phuket is being intensely developed, with many new hotels, apartments, and houses under construction. As of 2015 there were 47,475 hotel rooms, with another 4,400 rooms expected to be built by 2018. In July 2005, Phuket was voted one of the world’s top five retirement destinations by Fortune Magazine. There are thousands of expatriates living on Phuket, many of them retirees.
Transportation
Air
Phuket International Airport (HKT) commenced a 5.7 billion baht (US$185.7 million) expansion in September 2012, scheduled for completion on 14 February 2016. The Phuket Airport Authority has confirmed that the expansion of the international terminal will be completed deadline as promised. The airport will increase its annual handling capacity from 6.5 million to 12.5 million passengers, and add a new international terminal.
There is no rail line to Phuket. Trains run to nearby Surat Thani. Songthaews are a common mode of transport on Phuket. Phuket’s songthaews are larger than those found in other areas of Thailand. Songthaews are the cheapest mode of transportation from town to town. They travel between the town and beaches. There are also conventional bus services and motorbike taxis. The latter are found in large numbers in the main town and at Patong Beach. Traditional tuk-tuks have been replaced by small vans, mostly red, with some being yellow or green. Car taxis are quite expensive and charge flat rates between towns.
Bus
Phuket’s Bus Station 2 BKS Terminal is the long-distance arrivals hub for buses to and from Bangkok and other major Thai cities and provinces. Located four kilometres to the north of Phuket’s town centre and port, the complex is large and modern, linking with transportation by tuk-tuk, metered taxi, motorcycle taxi, songthaew, or local bus to the island’s beaches and resorts. There are daily scheduled buses from private and government run companies going to Phuket from Bangkok’s Mo Chit and Southern terminal stations.










